Unsupervised Clustering
Contents
- Motivation
- Load class 0 (“normal”) images
- Build and fit autoencoder
- Map the original images into the learned latent feature space
- Cluster analysis
Motivation
The “normal” (class 0) observations were generated from tiles of the original DDSM images, and so include a number of instances of chart annotations of the following sort found in the image background:
def plot_img_from_file(filename, ax, title=None):
img = plt.imread(filename)
ax.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
ax.axis('off')
if title is not None:
ax.set_title(title)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=5, figsize=(10,15))
axes = axes.ravel()
for ax, file in zip(axes, ['c311.png', 'c545.png', 'c578.png', 'c596.png', 'c1191.png']):
plot_img_from_file(f"data/train_images/{file}", ax)
fig.tight_layout()

While it was easy to remove uninformative observations that were mostly or entirely black based on the distribution of pixel intensities in the images, this approach was unsuccessful at sorting out observations with the sort of “misinformative” content shown above. Because these images contained positive content that would be easy for a CNN to recognize, and because only the normal-class images contained this type of content, we feared that the classifier would learn to associate annotative lettering with normal-class observations. The trained model would therefore perform poorly when used to classify the full images, in which chart annotations were not uncommon even in scans that contain abnormalities (masses or calcifications).
We decided to try to use a model to automate the process of identifying these “misinformative” images from the set of all normal-class observations. Since we did not have a large set of scans with lettering to use for training the model in a supervised fashion, we instead had to adopt an unsupervised method for identifying these images. We therefore trained an autoencoder on the normal images, expecting that it would identify the latent characteristics of the text annotations that we ourselves could recognize by sight. We then performed unsupervised clustering in the learned latent space to identify clusters of observations with these types of features.
Load class 0 (“normal”) images
'''IMPORT TRAINING LABELS'''
train_data_c0_df = pd.read_csv('data/training_data.csv')
train_data_c0_df = train_data_c0_df.loc[train_data_c0_df['class']==0,:]
train_data_c0_df = train_data_c0_df.drop(columns=['normal_class','class','Unnamed: 0'])
train_data_c0_df['filename'] = train_data_c0_df['id'].apply(lambda x: x+'.png')
'''IMPORT TEST LABELS'''
test_data_c0_df = pd.read_csv('data/test_data.csv')
test_data_c0_df = test_data_c0_df.loc[test_data_c0_df['class']==0,:]
test_data_c0_df['filename'] = test_data_c0_df['id'].apply(lambda x: x+'.png')
Build and fit autoencoder
Encoder
latent_dim = 150
img_dims = (128,128,3)
input_img = Input(shape=img_dims)
x = Conv2D(128, (3,3), padding='same', use_bias=False)(input_img)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Activation("relu")(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2))(x)
x = Conv2D(64, (3,3), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Activation("relu")(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2))(x)
x = Conv2D(32, (3,3), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Activation("relu")(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2))(x)
shape_before_flattening = K.int_shape(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(256)(x)
z = Dense(latent_dim, activation='relu')(x)
encoder = Model(input_img, z)
encoder.summary()
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, 128, 128, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 128) 3456
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_1 (Batch (None, 128, 128, 128) 512
_________________________________________________________________
activation_1 (Activation) (None, 128, 128, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2 (None, 64, 64, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 64, 64, 64) 73728
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_2 (Batch (None, 64, 64, 64) 256
_________________________________________________________________
activation_2 (Activation) (None, 64, 64, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_2 (MaxPooling2 (None, 32, 32, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_3 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 32) 18432
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_3 (Batch (None, 32, 32, 32) 128
_________________________________________________________________
activation_3 (Activation) (None, 32, 32, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_3 (MaxPooling2 (None, 16, 16, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 8192) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 256) 2097408
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 150) 38550
=================================================================
Total params: 2,232,470
Trainable params: 2,232,022
Non-trainable params: 448
_________________________________________________________________
Decoder
decoder_input = Input(K.int_shape(z)[1:])
x = Dense(256)(decoder_input)
x = Dense(np.prod(shape_before_flattening[1:]), activation='relu')(x)
x = Reshape(shape_before_flattening[1:])(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2,2))(x)
x = Conv2DTranspose(32, (3,3), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Activation("relu")(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2,2))(x)
x = Conv2DTranspose(64, (3,3), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Activation("relu")(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2,2))(x)
x = Conv2DTranspose(128, (3,3), padding='same', activation='relu')(x)
decoder_output = Conv2D(3, 1, activation='sigmoid')(x)
decoder = Model(decoder_input, decoder_output)
decoder.summary()
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_2 (InputLayer) (None, 150) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 256) 38656
_________________________________________________________________
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 8192) 2105344
_________________________________________________________________
reshape_1 (Reshape) (None, 16, 16, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
up_sampling2d_1 (UpSampling2 (None, 32, 32, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose_1 (Conv2DTr (None, 32, 32, 32) 9216
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_4 (Batch (None, 32, 32, 32) 128
_________________________________________________________________
activation_4 (Activation) (None, 32, 32, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
up_sampling2d_2 (UpSampling2 (None, 64, 64, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose_2 (Conv2DTr (None, 64, 64, 64) 18432
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_5 (Batch (None, 64, 64, 64) 256
_________________________________________________________________
activation_5 (Activation) (None, 64, 64, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
up_sampling2d_3 (UpSampling2 (None, 128, 128, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose_3 (Conv2DTr (None, 128, 128, 128) 73856
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_4 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 3) 387
=================================================================
Total params: 2,246,275
Trainable params: 2,246,083
Non-trainable params: 192
_________________________________________________________________
Autoencoder
ae_out = decoder(encoder(input_img))
ae = Model(input_img, ae_out)
ae.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy')
ae.summary()
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, 128, 128, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
model_1 (Model) (None, 150) 2232470
_________________________________________________________________
model_2 (Model) (None, 128, 128, 3) 2246275
=================================================================
Total params: 4,478,745
Trainable params: 4,478,105
Non-trainable params: 640
_________________________________________________________________
batch_size = 128
epochs = 30
steps_per_epoch = int(np.ceil(len(train_data_c0_df) / batch_size))
validation_steps = int(np.ceil(len(test_data_c0_df) / batch_size))
train_datagen = image.ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_datagen = image.ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
directory='data/train_images',
dataframe=train_data_c0_df,
x_col="filename",
batch_size=batch_size,
class_mode="input",
target_size=img_dims[:2],
color_mode="rgb",
shuffle=True,
seed=42
)
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
directory='data/test_images',
dataframe=test_data_c0_df,
x_col="filename",
batch_size=batch_size,
class_mode="input",
target_size=img_dims[:2],
color_mode="rgb",
shuffle=True,
seed=42
)
Found 48596 images.
Found 13360 images.
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=5, verbose=0, mode='auto')
history = ae.fit_generator(train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=steps_per_epoch,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
callbacks=[early_stopping],
validation_data=test_generator,
validation_steps=validation_steps)
Epoch 1/30
380/380 [==============================] - 496s 1s/step - loss: 0.5609 - val_loss: 0.5560
Epoch 2/30
380/380 [==============================] - 479s 1s/step - loss: 0.5567 - val_loss: 0.5546
Epoch 3/30
380/380 [==============================] - 478s 1s/step - loss: 0.5561 - val_loss: 0.5628
Epoch 4/30
380/380 [==============================] - 478s 1s/step - loss: 0.5558 - val_loss: 0.5544
Epoch 5/30
380/380 [==============================] - 476s 1s/step - loss: 0.5556 - val_loss: 0.5563
Epoch 6/30
380/380 [==============================] - 478s 1s/step - loss: 0.5553 - val_loss: 0.5543
Epoch 7/30
380/380 [==============================] - 476s 1s/step - loss: 0.5552 - val_loss: 0.5537
Epoch 8/30
380/380 [==============================] - 478s 1s/step - loss: 0.5552 - val_loss: 0.5565
Epoch 9/30
380/380 [==============================] - 476s 1s/step - loss: 0.5551 - val_loss: 0.5531
Epoch 10/30
380/380 [==============================] - 477s 1s/step - loss: 0.5549 - val_loss: 0.5537
Epoch 11/30
380/380 [==============================] - 476s 1s/step - loss: 0.5549 - val_loss: 0.5559
Epoch 12/30
380/380 [==============================] - 476s 1s/step - loss: 0.5548 - val_loss: 0.5532
Epoch 13/30
380/380 [==============================] - 476s 1s/step - loss: 0.5548 - val_loss: 0.5536
Epoch 14/30
380/380 [==============================] - 475s 1s/step - loss: 0.5547 - val_loss: 0.5537
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=3, figsize=(12,8))
for i, imgnum in enumerate(['c311', 'c545', 'c578']):
filepath = f"data/train_images/{imgnum}.png"
img = plt.imread(filepath)
img = resize(img, img_dims, mode='constant')
axes[0,i].imshow(img)
axes[0,i].set_title(f"Original: {imgnum}")
axes[0,i].axis('off')
# Map original image into the latent space
img_encoded = encoder.predict(np.array([img]))
img_decoded = decoder.predict(img_encoded)[0]
axes[1,i].imshow(img_decoded)
axes[1,i].set_title("Reconstructed")
axes[1,i].axis('off');

The reconstructed images passed through the autoencoder only vaguely resemble the original images, potentially suggesting that the model was unable to learn to identify the alphanumeric annotations as conceptually distinct from the desired content (breast tissue). We also trained several Variational Autoencoder models, though they performed no better than this vanilla autoencoder.
Map the original images into the learned latent feature space
encodings = []
ids = []
idx = []
for row in train_data_c0_df.iterrows():
idx.append(row[0])
ids.append(row[1]['id'])
filepath = "data/train_images/" + row[1]['filename']
img = plt.imread(filepath)
img = resize(img, img_dims, mode='constant')
encodings.append(encoder.predict(np.array([img])).squeeze().tolist())
# prepare DataFrame with latent feature values for each image in the training set
encodings_df = pd.DataFrame({'idx':idx, 'id':ids, 'encodings':encodings}).set_index('idx')
encodings_df = train_data_c0_df.merge(encodings_df, left_index=True, right_index=True)
encodings_df = encodings_df.drop(columns='id_y')
encodings_feats = encodings_df['encodings'].apply(pd.Series)
encodings_feats = encodings_feats.rename(columns = lambda x : 'latentvar_' + str(x+1))
encodings_df = encodings_df.merge(encodings_feats, left_index=True, right_index=True)
Cluster analysis
latentvar_cols = [col for col in encodings_df.columns if col.startswith('latentvar_')]
X = encodings_df[latentvar_cols].copy()
y = encodings_df['id_x'].copy()
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
DBSCAN
We first use DBSCAN to identify similar observations to the five displayed above. Since we do not know the shape of the latent feature space, and do not even roughly know the number of observations that only contain annotation text (i.e. that should be removed), DBSCAN is an ideal clustering algorithm in that it does not require that we specify the number of clusters in advance, and does not impose assumptions on the shape of the clusters.
Using the default parameters, the DBSCAN algorithm identifies all five observations as “noisy” (not belonging to a cluster). We therefore increased the maximum distance between samples for them to be considered in the same neighborhood, though obtained the same result.
dbscan_results = DBSCAN(eps=0.9).fit(X)
# distribution of cluster membership (-1 represents "noisy" observations)
pd.Series(dbscan_results.labels_).value_counts()
-1 35617
0 11043
1 1023
2 214
13 25
3 20
5 19
36 17
32 14
48 14
18 14
37 14
33 14
52 14
57 12
89 11
53 11
28 11
46 10
35 10
25 9
47 9
7 9
30 9
50 8
12 8
40 8
78 8
39 8
20 8
...
29 5
60 5
27 5
58 5
26 5
88 5
56 5
24 5
55 5
23 5
15 5
17 5
44 5
51 5
82 5
49 5
75 5
16 5
14 5
77 5
45 5
76 5
54 4
86 4
83 4
81 4
79 4
100 3
43 3
42 3
Length: 102, dtype: int64
dbscan_df = pd.DataFrame({'img_id': y, 'cluster_id': dbscan_results.labels_})
dbscan_df[dbscan_df['img_id'].isin(['c311', 'c545', 'c578', 'c596', 'c1191'])]
| img_id | cluster_id | |
|---|---|---|
| 310 | c311 | -1 |
| 544 | c545 | -1 |
| 577 | c578 | -1 |
| 595 | c596 | -1 |
| 1190 | c1191 | -1 |
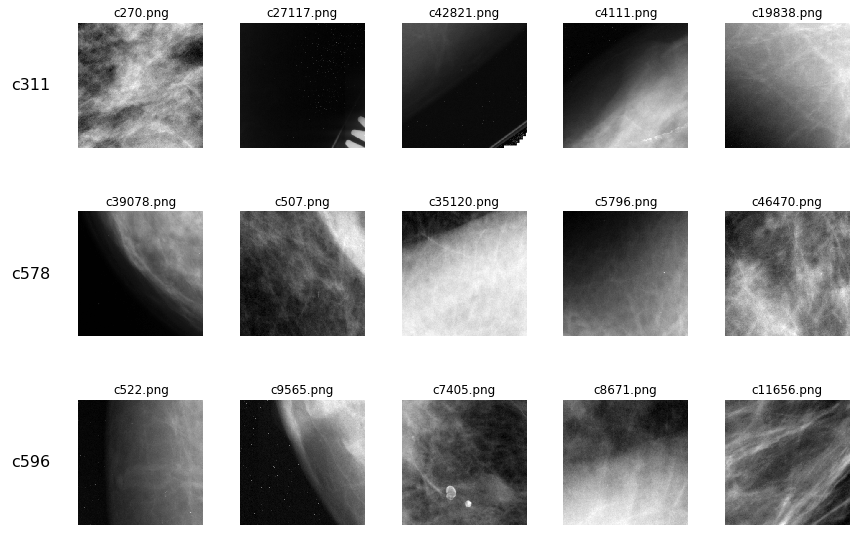
k nearest neighbors
Since DBSCAN identified all of the observations as not belonging to a neighborhood, we instead tried finding the k nearest neighbors in latent space to each of the original observations using a k-dimensional tree. However, the results confirm that the observations do not appear to cluster with other observations that are in any way similar.
kdt = KDTree(X, metric='euclidean')
# get k nearest neighbors to each original image
K = 5
orig_imgs = ['c311', 'c578', 'c596']
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=len(orig_imgs), ncols=K, figsize=(12,8))
for i, orig_img in enumerate(orig_imgs):
dists, idxs = kdt.query(X[encodings_df['id_x']==orig_img,:], k=K)
nbr_imgs = encodings_df.loc[idxs.squeeze(),'filename'].tolist()
for j, imgfile in enumerate(nbr_imgs):
plot_img_from_file(f"data/train_images/{imgfile}", axes[i,j], f"{imgfile}")
for ax, row in zip(axes[:,0], orig_imgs):
ax.annotate(row, xy=(0, 0.5), xytext=(-ax.yaxis.labelpad+2, 0),
xycoords=ax.yaxis.label, textcoords='offset points',
fontsize=16, ha='right', va='center')
fig.tight_layout()